The booming popularity of cannabis and its derivatives in recent years has sparked a renewed interest in understanding the connection between this plant and our own bodies. As the discussions surrounding this controversial plant continue to evolve, scientists and researchers have been investigating a fascinating biological system within our bodies and pretty much all living creatures, known as the endocannabinoid system. This complex system plays a crucial role in maintaining our health and well-being, and its interplay with cannabis has become a topic of great intrigue as cannabis is one of the only other cannabinoid creators. In this article, we will delve into the relationship between the endocannabinoid system and cannabis, shedding light on the scientific discoveries that are reshaping our understanding of this ancient plant and its potential benefits. So, let's embark on this journey of unraveling the secrets of the endocannabinoid system and exploring how it interacts with cannabis.
How Cannabis Interacts with the Endocannabinoid System
he endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex network of receptors and molecules found throughout our bodies that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. Interestingly, the ECS is also the target of compounds found in cannabis, leading to its widespread use for medicinal and recreational purposes. Understanding how cannabis interacts with the ECS can shed light on its effects and potential therapeutic benefits.
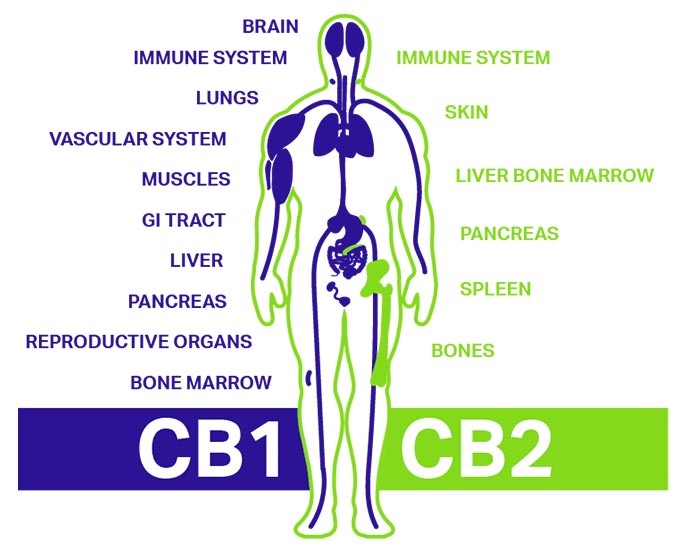
The key components of the ECS are its receptors, known as CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are mainly found in the immune system and peripheral tissues. When cannabis is consumed, the cannabinoids, such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), interact with these receptors.
THC, the psychoactive component of cannabis, binds to CB1 receptors, causing the characteristic euphoria and altered perception associated with cannabis use. On the other hand, CBD does not directly bind to the CB1 or CB2 receptors but modulates their activity. This is why CBD is non-intoxicating and is often used for its potential therapeutic benefits, such as reducing pain and inflammation.
Moreover, the endocannabinoid system is not solely influenced by cannabinoids from cannabis. Our bodies produce their own endocannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-AG, to regulate various physiological processes like mood, sleep, and appetite. These endocannabinoids bind to the CB1 and CB2 receptors, just like the cannabinoids from cannabis.
Overall, cannabis exerts its effects through its interaction with the endocannabinoid system. This intricate interplay between cannabinoids and ECS receptors contributes to the wide range of therapeutic uses of cannabis, from pain relief to the management of neurological conditions. Research into cannabis and the endocannabinoid system is ongoing, offering a promising avenue for understanding this complex system and the potential benefits of cannabis as a medicine.

Benefits of Cannabis on the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabis has been a controversial topic for many years, but recent research has shed light on its potential benefits on the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system, found in the human body, plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes such as sleep, appetite, pain, and inflammation. THC and CBD, two compounds found in cannabis, interact with the receptors of the endocannabinoid system, leading to potential therapeutic benefits.
One of the key benefits of cannabis on the endocannabinoid system is its ability to provide pain relief. THC activates the CB1 receptors in the brain, which helps to reduce pain sensation. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions such as arthritis or fibromyalgia. CBD, on the other hand, influences the receptors in the immune system, reducing inflammation and providing relief from pain.
In addition to pain relief, cannabis has also shown promise in treating mental health disorders. Studies have suggested that CBD can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression by influencing the endocannabinoid system. CBD interacts with the receptors in the brain responsible for regulating mood and emotions, leading to a potential reduction in anxiety and improved mental well-being.
Furthermore, cannabis may also benefit individuals with neurological disorders such as epilepsy. CBD has been found to have anticonvulsant properties, reducing the frequency and severity of seizures. This could be a game-changer for patients who have not responded well to traditional medications.
Although further research is needed to fully understand the effects of cannabis on the endocannabinoid system, the potential benefits are promising. By targeting the receptors of this system, cannabis has the potential to provide relief for a range of conditions, from pain and inflammation to mental health disorders and epilepsy. It is important, however, to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating cannabis as part of any treatment plan.
Cannabinoids and Their Effects on Endocannabinoid Receptors
Cannabinoids are a diverse group of chemical compounds that can be found in the cannabis plant and also produced naturally in our bodies. These compounds interact with our endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and molecules that regulates various physiological processes such as appetite, pain sensation, mood, and immune response. This intricate system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and overall well-being.
One of the primary functions of the endocannabinoid system is to receive and transmit signals, which are facilitated by specialized receptors called CB1 and CB2 receptors. When cannabinoids, either from the cannabis plant or produced within our bodies, bind to these receptors, they can influence how the body responds to various stimuli. For instance, activation of CB1 receptors in the brain may result in the feeling of euphoria commonly associated with cannabis use, while activation of CB2 receptors in immune cells can modulate inflammation and immune response.
Research on cannabinoids and their effects on endocannabinoid receptors has provided valuable insights into new therapeutic approaches for various conditions. For example, CBD (cannabidiol), a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis, has shown potential as an anti-inflammatory agent and has been used to alleviate symptoms of chronic pain and epilepsy. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), on the other hand, is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis and has been found to have analgesic properties.
Understanding the intricate relationship between cannabinoids and endocannabinoid receptors is still an ongoing area of study, and scientists are constantly unraveling the complexities of this system. As research advances, it opens up exciting possibilities for harnessing the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids to treat a wide range of health conditions. The interplay between the endocannabinoid system and cannabis is a captivating field that continues to intrigue scientists and offers hope for novel therapeutic interventions in the future.
How CBD and THC Influence the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system, found in all mammals, plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within the body. It is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that help regulate various biological functions such as mood, appetite, pain sensation, and immune response. Interestingly, cannabis, particularly its two primary compounds CBD and THC, can interact with this system and influence its activity.
CBD, or cannabidiol, is a non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants. It has been shown to indirectly influence the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting the breakdown of anandamide, an endocannabinoid known to promote feelings of happiness and well-being. This leads to elevated levels of anandamide, which can potentially have a positive impact on mood and overall emotional state.
On the other hand, THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the psychoactive compound in cannabis that creates the notorious "high" associated with marijuana. THC binds directly to CB1 receptors in the endocannabinoid system, leading to various effects on the body and mind, including euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception of time. Its interaction with the CB1 receptors can also affect memory, coordination, and appetite.
Both CBD and THC have been the subject of extensive scientific research in recent years, as their potential therapeutic benefits have gained recognition. CBD, with its non-intoxicating properties, has shown promise in treating conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, and chronic pain. THC, on the other hand, has demonstrated potential in managing pain, nausea, and stimulating appetite in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Understanding how CBD and THC influence the endocannabinoid system is crucial not only for medical advancements but also for the development of safe and effective cannabis-based products. Further research is needed to fully comprehend these compounds' interactions with the endocannabinoid system and to harness their therapeutic potentials while minimizing any potential undesired effects.
The Future of Cannabis Research and the Endocannabinoid System
As the acceptance and legalization of cannabis continues to grow, so does the interest in understanding the science behind it. One of the most fascinating aspects of cannabis research is the study of the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network of receptors and molecules found within our bodies. The ECS plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, such as mood, appetite, pain, and sleep, and cannabis compounds, like THC and CBD, interact with these receptors.
The future of cannabis research lies in exploring the intricate relationship between the ECS and cannabis. Scientists are working tirelessly to uncover the potential benefits and limitations of cannabinoids for various medical conditions. For instance, studies have shown that CBD, a non-psychoactive component of cannabis, may have therapeutic effects on epilepsy, anxiety, and chronic pain. By understanding how cannabis interacts with the ECS, researchers can develop targeted treatments tailored to individual needs.
Furthermore, the exploration of the ECS opens up exciting possibilities for the development of new drugs. Cannabis compounds, like THC and CBD, are just two of the many cannabinoids found in the plant. With technological advancements and a deeper understanding of the ECS, scientists may discover other cannabinoids and their potential therapeutic properties. This could lead to more effective and specialized medications that target specific conditions and alleviate symptoms with minimal side effects.
However, to fully understand the benefits and risks of cannabis use, further research is needed. Clinical trials and long-term studies are essential to gather comprehensive data on the effects of cannabinoids on various systems in the body. Additionally, as cannabis legalization spreads across the globe, it is crucial to establish standardized regulations and guidelines for cannabis research to ensure quality and consistency across studies.
In conclusion, the future of cannabis research is closely tied to the exploration of the endocannabinoid system. By understanding how cannabis compounds interact with this complex network within our bodies, scientists can unlock new treatments and medications that have the potential to improve the lives of many. As research continues, it is important to support and encourage advancements in this field to harness the full potential of cannabis and the endocannabinoid system.
